Hanyang University
College of Engineering
 NewsFaculty
NewsFaculty
Faculty
| Developing Cell Death Inducer for Cancer Immunotherapy | |
|---|---|
|
작성자 : 한양대학교 공과대학(help@hanyang.ac.kr) 작성일 : 21.06.04 조회수 : 290 URL : |
|
|
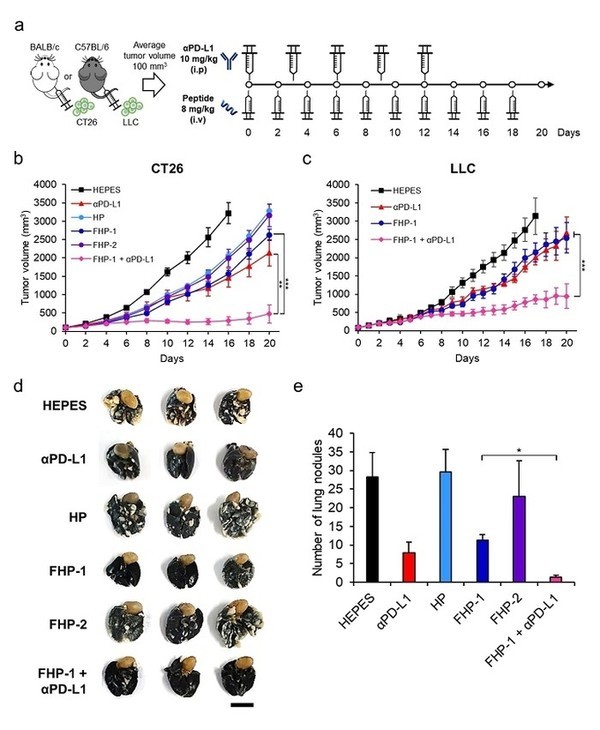
Professor Yoon Chae-ok of the Department of Bioengineering at Hanyang University and Yeu-Chun Kim of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST have jointly developed a peptide-based immunogenic cell-death inducer that works with immuno-barrier inhibitors to treat cancer. The peptide developed by the research team breaks the mitochondrial outer membrane of the cancer cells and increases the active oxygen concentration, and oxidative stress stimulates the endoplasmic reticulum to induce the killing of immunogenic cells.
Immune-barrier inhibitors block immune barriers that inhibit the activity of immune cells in T cells (CTLA-4, PD-1) and cancer cells (PD-L1) and activate immune cells. A variety of immunosuppressants have been used in patients since its first approval by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2011.
Furthermore, when the peptide and immune barrier inhibitor, anti-PD-L1, were administered in combination with animal experiments, tumor suppressor ability was improved compared with a single administration, and metastasis to the lungs was reduced by an activated immune reaction.
|
|
| 이전글 | Prof. Kim Sun-jeong Selected for the 9th Baiknam Academy Award |
| 다음글 | Identifying Social Unrest and Sensitivity Reduction to COVID-19 with Deep Learning the First Time |
|
|